Understanding Monomeric, Polymeric, and Cast Vinyl Film
Monomeric Vinyl:
- Ideal for short-term applications and flat surfaces.
- Economical choice for temporary signage, promotional displays, and indoor graphics.
- Offers good conformability but may not withstand extreme weather conditions as well as cast or polymeric vinyl.
Polymeric Vinyl:
- Designed for medium to long-term outdoor applications with moderate curves and contours.
- Offers better durability and weather resistance compared to monomeric viny
- Suitable for vehicle graphics, outdoor signage, and architectural elements where extended longevity is require
Cast Vinyl:
- Engineered for long-term outdoor applications and complex curve
- Premium choice for vehicle wraps, outdoor signage, and architectural element
- Provides superior conformability and durability, maintaining its integrity even in harsh environments.
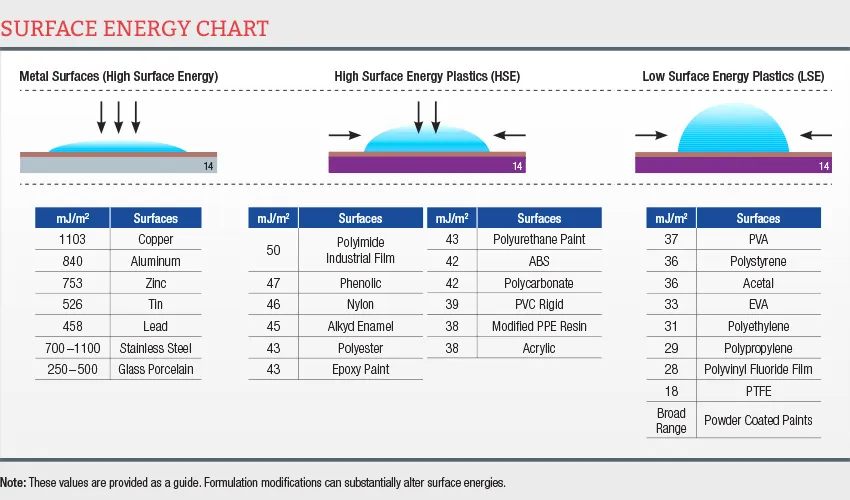
Understanding Surface Energy
The surface energy of materials can be classified into three groups: high, medium and low surface energy.
High Surface EnergyMolecules on the surface are so strongly attracted to each other that they will very happily be attracted to liquid molecules as well. As a result, these materials are relatively easy to wet out and, in turn, to bond. High surface energy materials have surface energies on the order of 100s or 1000s of dynes/cm and include many metals and glass. |  |
Medium Surface EnergyEverything is relative. Somewhere between perfectly wet-out films and perfectly spherical droplets, we define medium surface energy. These are materials typically 36 dynes/cm up to about 300 dynes/cm. Many engineered plastics have surface energies in this range, as do natural materials such as wood, stone or concrete. |  |
Low Surface EnergyMolecules on the surface of low-surface-energy materials are quite happy the way they are. There is very little attraction to any molecule, especially adhesive molecules. Materials with a surface energy below 36 dynes/cm are considered low surface energy and are very difficult to bond. These include polyolefin plastics such as polypropylene and polyethylene as well as “non-stick” surfaces such as polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE). |  |